
 [video TW](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3xtN129sOXY&t=40s)
# Make yeast
- dry yeast (5gr)
- distilled water ( 30ml)
- 00 type flour (60 gr)
Talas and Banggkuang untuk diabetes
# [Venturi pump for oxygenator](https://aquaculturefrance.com/en/)
[video TW](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3xtN129sOXY&t=40s)
# Make yeast
- dry yeast (5gr)
- distilled water ( 30ml)
- 00 type flour (60 gr)
Talas and Banggkuang untuk diabetes
# [Venturi pump for oxygenator](https://aquaculturefrance.com/en/)


 # [Airlift pump vs pump](https://aquaculturemag.com/2023/12/25/engineered-airlift-pumps-can-help-aquaculture-systems-to-perform-better/)
# [Airlift pump vs pump](https://aquaculturemag.com/2023/12/25/engineered-airlift-pumps-can-help-aquaculture-systems-to-perform-better/)
 [airlift 300x](https://www.reddit.com/r/Aquaculture/comments/1qd63bx/100x_cheaper_simpler_and_more_reliable_than_pumps/)
[airlift 300x](https://www.reddit.com/r/Aquaculture/comments/1qd63bx/100x_cheaper_simpler_and_more_reliable_than_pumps/)
 https://www.aesweb.org/files/Webinars/RAStech_2022_Presentation_3_Briquet.pdf
https://repository.lsu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=3941&context=gradschool_theses
## [Traditional airlift pumps](https://www.globalseafood.org/advocate/rectangular-airlift-pump-design-outperforms-cylindrical-units/)
The traditional airlift pump injects air into a cylindrical chamber/pipe that is partially or fully submerged in a fluid, typically water.
The air is injected into the fluid-filled cylinder at the side or in the center of the cylinder, above the intake.
The cylinder acts as a mixing chamber for the water and injected air.
In a 1994 World Aquaculture article, the author explained that the air-water mixture is less dense than, and therefore displaced by,
the surrounding water. The air-water mixture is forced out of the mixing chamber and through the discharge outlet at the top of the cylinder.
A steady flow of injected air produces a constant air-water mixture that is continually pushed to the surface and creates the pumping action of the airlift pump.
Pumping rates in airlift pumps are limited by cylinder diameter and the air injection methods required for cylindrical mixing chambers. To increase
flow rates beyond a single cylinder’s capacity, the output of several cylinders must be combined. This requires a cumbersome assembly of multiple airlift
cylinders that must be connected with potentially significant space requirements. Each cylinder needs its own independent air injector and, as a result,
an extensive air delivery system is necessary.
For any given air flow rate, friction and inline pressure increase as the length of the air distribution pipe (delivery system) increases. Essentially,
the efficiency of air delivery to the pumping cylinders drops as the size of the air distribution system is increased to include multiple airlift cylinders.
A single, compact and efficient airlift with high-volume output would be desirable.
## Rectangular airlifts
The geometry of a rectangular riser has some advantages over cylinders for building airlift pumps. Cylinders and square tubes have the same surface area:volume ratio when the diameter of the cylinder equals the length of the square’s sides. But when a rectangular riser is used, the surface area:volume ratio can be much lower than those of cylinders and square tubes, depending on the dimensions of the rectangle. The larger the dimensions of the rectangular perimeter, the lower the surface area:volume ratio becomes.
For a rectangular riser with perimeter dimensions large enough to tightly encompass 40 cylinders, the surface area:volume ratio would be five times less than that for the 40 cylinders combined (Table 1). Furthermore, if made of the same material, 40 cylinders would be over four times heavier than the rectangular riser. Surface area is important with respect to fluid flow and resistance. As surface area increases, resistance to fluid flow increases. A lower surface area:volume ratio means less fluid resistance, and higher flow rates are possible.
- RAS use pumps 90%, airlift pump 10%
- [airlift pump use in water recirulation (300x ?/day)](https://www.raschile.cl/copia-de-reuse)
- lift ideally 20-30cm, maximum 50-70cm
- can not use in wash drum filter
- saturated the water with oxygen and degass CO2
- not efficient
- air-to-water ratio 1:1 or max 1.5 : 1
- compressor use rotary instead of vortex compressor
- Prepeller pumps
# [Freeze drying is the removal of water by sublimation from the frozen state (ice).](https://www.ellab.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/the-freeze-drying-theory-and-process_ellab-whitepaper.pdf)
In this process, the food is first frozen and then subjected to a high vacuum, whereby the water ice evaporates without melting.
The water vapor released is condensed on the surface of a condenser at very low temperature. The heat needed for sublimation is supplied by radiation or conduction.
Freeze drying occurs in two stages: sublimation of the ice, and desorption of the moisture adsorbed in the dry matrix.
A model for lyophilization kinetics in a greatly simplified system is developed. Applications of freeze drying in the food industry are reviewed, and batch and continuous
freeze dryers are described. Microwave freeze drying is discussed.
Freeze concentration is the removal of water from a frozen food liquid as ice crystals. Since freeze concentration occurs without heating or boiling, thermal damage and
loss of volatile aromas are largely avoided. The main disadvantage of freeze concentration is the loss of solute, which may be considerable at high concentration ratio.
PRODUCTS BEING FREEZE DRIED:
Pharmaceuticals
Homeopathic Remedies
Camping Food
Pet Food
Coffee
Mushrooms
Guacamole/Salsa
Herbs
Fruits & Veggies
Meats
Fish
Ice Cream
Eggs
Baby Food
Easy-to-make Meals
Soups
Cannabis & Related Products
mangrove soils
https://www.aesweb.org/files/Webinars/RAStech_2022_Presentation_3_Briquet.pdf
https://repository.lsu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=3941&context=gradschool_theses
## [Traditional airlift pumps](https://www.globalseafood.org/advocate/rectangular-airlift-pump-design-outperforms-cylindrical-units/)
The traditional airlift pump injects air into a cylindrical chamber/pipe that is partially or fully submerged in a fluid, typically water.
The air is injected into the fluid-filled cylinder at the side or in the center of the cylinder, above the intake.
The cylinder acts as a mixing chamber for the water and injected air.
In a 1994 World Aquaculture article, the author explained that the air-water mixture is less dense than, and therefore displaced by,
the surrounding water. The air-water mixture is forced out of the mixing chamber and through the discharge outlet at the top of the cylinder.
A steady flow of injected air produces a constant air-water mixture that is continually pushed to the surface and creates the pumping action of the airlift pump.
Pumping rates in airlift pumps are limited by cylinder diameter and the air injection methods required for cylindrical mixing chambers. To increase
flow rates beyond a single cylinder’s capacity, the output of several cylinders must be combined. This requires a cumbersome assembly of multiple airlift
cylinders that must be connected with potentially significant space requirements. Each cylinder needs its own independent air injector and, as a result,
an extensive air delivery system is necessary.
For any given air flow rate, friction and inline pressure increase as the length of the air distribution pipe (delivery system) increases. Essentially,
the efficiency of air delivery to the pumping cylinders drops as the size of the air distribution system is increased to include multiple airlift cylinders.
A single, compact and efficient airlift with high-volume output would be desirable.
## Rectangular airlifts
The geometry of a rectangular riser has some advantages over cylinders for building airlift pumps. Cylinders and square tubes have the same surface area:volume ratio when the diameter of the cylinder equals the length of the square’s sides. But when a rectangular riser is used, the surface area:volume ratio can be much lower than those of cylinders and square tubes, depending on the dimensions of the rectangle. The larger the dimensions of the rectangular perimeter, the lower the surface area:volume ratio becomes.
For a rectangular riser with perimeter dimensions large enough to tightly encompass 40 cylinders, the surface area:volume ratio would be five times less than that for the 40 cylinders combined (Table 1). Furthermore, if made of the same material, 40 cylinders would be over four times heavier than the rectangular riser. Surface area is important with respect to fluid flow and resistance. As surface area increases, resistance to fluid flow increases. A lower surface area:volume ratio means less fluid resistance, and higher flow rates are possible.
- RAS use pumps 90%, airlift pump 10%
- [airlift pump use in water recirulation (300x ?/day)](https://www.raschile.cl/copia-de-reuse)
- lift ideally 20-30cm, maximum 50-70cm
- can not use in wash drum filter
- saturated the water with oxygen and degass CO2
- not efficient
- air-to-water ratio 1:1 or max 1.5 : 1
- compressor use rotary instead of vortex compressor
- Prepeller pumps
# [Freeze drying is the removal of water by sublimation from the frozen state (ice).](https://www.ellab.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/the-freeze-drying-theory-and-process_ellab-whitepaper.pdf)
In this process, the food is first frozen and then subjected to a high vacuum, whereby the water ice evaporates without melting.
The water vapor released is condensed on the surface of a condenser at very low temperature. The heat needed for sublimation is supplied by radiation or conduction.
Freeze drying occurs in two stages: sublimation of the ice, and desorption of the moisture adsorbed in the dry matrix.
A model for lyophilization kinetics in a greatly simplified system is developed. Applications of freeze drying in the food industry are reviewed, and batch and continuous
freeze dryers are described. Microwave freeze drying is discussed.
Freeze concentration is the removal of water from a frozen food liquid as ice crystals. Since freeze concentration occurs without heating or boiling, thermal damage and
loss of volatile aromas are largely avoided. The main disadvantage of freeze concentration is the loss of solute, which may be considerable at high concentration ratio.
PRODUCTS BEING FREEZE DRIED:
Pharmaceuticals
Homeopathic Remedies
Camping Food
Pet Food
Coffee
Mushrooms
Guacamole/Salsa
Herbs
Fruits & Veggies
Meats
Fish
Ice Cream
Eggs
Baby Food
Easy-to-make Meals
Soups
Cannabis & Related Products
mangrove soils
 o
https://i0.wp.com/randomnerdtutorials.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/DHT22_RaspberryPi_ESP8266.jpg?quality=100&strip=all&ssl=1
# [Nanopb](https://jpa.kapsi.fi/nanopb/)
# What is distilled water?
Distilled water is a highly purified form of water that has been stripped of almost all of its impurities,
including minerals, salts, and other organic and inorganic compounds. Through the process of distillation, water is boiled,
turned into steam, and then cooled and condensed back into a liquid state. This process leaves behind contaminants,
resulting in water that is essentially pure H₂O.
How is distilled water made?
The process of creating distilled water mimics the natural water cycle and involves these key steps:
Boiling: Tap water or spring water is heated in a boiler until it reaches its boiling point and transforms into steam.
Evaporation: As the water evaporates into steam, it leaves behind dissolved solids, such as salts, minerals (like calcium and magnesium), and other non-volatile contaminants.
Condensation: The steam is then channeled into a separate cooling system or condenser. As the steam cools, it reverts to its liquid form.
Collection: The resulting liquid, now distilled water, is collected in a clean, sterile container.
What is the difference between distilled and purified water?
While both are clean forms of drinking water, there is a key distinction:
Distilled Water: This is a type of purified water that is created through the specific process of distillation (boiling and condensing).
This process removes nearly all minerals and other impurities.
Purified Water: This is a broader category of water that has been treated to remove impurities. Purification methods can include distillation,
reverse osmosis, deionization, or carbon filtration. The key difference is that some purification methods may not remove all minerals as effectively as distillation.
For water to be labeled as "purified," it must meet certain standards of purity, but it is not necessarily mineral-free.
https://www.axilscientific.com/products/chemicals/biological-buffers/2x-laemmli-sample-buffer-ph-68-biotechnology-grade-p-buf-5240.html
# Modbus sensors
are industrial devices using the standard Modbus protocol for digital communication, allowing them to send accurate data (like temperature, humidity, pressure, air quality)
over networks (RS485, TCP) to controllers (PLCs, BMS) using simple, cost-effective cabling, enabling daisy-chaining up to 247 devices for efficient data exchange in automation systems,
unlike analog sensors that need separate wiring for each signal.
[modbus esphome -1](https://esphome.io/components/modbus_controller/)
[modbus esphome -2 ](https://esphome.io/components/modbus/)
[esphome yaml modbus](https://github.com/mortenx/modbustcp_wifi_esphome/tree/60959a6fdde990ced413398072f1628c7e513b23)
[esphome in python](https://github.com/esphome/esphome/tree/dev/esphome)
https://ioninja.com/downloads/archive/ioninja/ioninja-5.9.1/
https://www.segger.com/products/debug-probes/j-link/technology/about-real-time-transfer/
STC-3008 Dual Digital Temperature Controller Two Relay Output 12V 24V 220V Thermoregulator Thermostat Heater Cooler With Probe
STC-3008 Dual Relay Digital Thermostat Controller NTC Sensor 12V 24V 110V 220V Adjustable Heating Cooling Switch
STC-8080A+ Refrigeration Temperature Controller Digital Thermostat for Freezer Cold Storage Defrost Fridge Use
Refrigeration Temperature Controller STC 8080A with Cooling Defrost and Over Temperature Alarm for Freezer Cold Room
STC-9200A/EK-3030 Temperature Controller for Refrigeration and Defrost Fans
Stainless Steel Electric Heating Tube 220V High-Temperature Grill & Oven Heater Rod for BBQ and Industrial Equipment
220V Digital Temperature Controller EK-3010/EK-3020/EK-3030 Refrigerator Refrigeration Defrost Thermostat Sensor
Upgraded heating cable transparent floor heating wire 100m 12K 33 ohm / M carbon electric heating cable
5/10/20/25/50/200/500/1000ml Class A Borosilicate Glass Lab Clear Volumetric Flask With Head Stopper
Yieryi MH1230A AC220V Digital Temperature Controller Thermocouple -40 ~ 120 Degrees Thermostat Refrigeration Heating Regulator
pH 4
Potassium Citrate 2.63g
Citric acid monohydrate 3.45g
(if using anhydrous citric acid, use 3.15g)
pH 7
Potassium Citrate 7.14g
Citric acid monohydrate 0.35g
(if using anhydrous citric acid, use 0.32g)
Class A Volumetric Flask (250mL)
LiveSeafood, [1/14/26 10:12 PM]
Excellent question. Preparing precise pH buffers from food-grade ingredients is a common need in food science, home brewing, and artisanal fermentation labs. While "food-grade" limits the chemicals we can use, we can achieve good approximations.
Critical Note: Food-grade chemicals have lower purity (typically 97-99%) than lab-grade (>99.9%). This, along with variations in mineral content of water, will affect the absolute accuracy. For critical work, always verify the pH with a recently calibrated meter.
Here are the calculations and methods for the three buffers at 25°C.
---
1. pH 4.01 Buffer (Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate, 0.05M)
This is the most straightforward, as the primary ingredient is available as a pH standard in food-grade form.
· Food-Grade Ingredient: Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate (KHP). It's commonly used as an acidulant and stabilizer (E336).
· Formula: KHC₈H₄O₄
· Molecular Weight: 204.22 g/mol
Calculation for 1 Liter of 0.05M Solution:
Moles = Molarity × Volume = 0.05 mol/L × 1 L = 0.05 mol
Mass = Moles × Molecular Weight = 0.05 mol × 204.22 g/mol = 10.211 g
Preparation:
1. Weigh 10.21 grams of food-grade potassium hydrogen phthalate.
2. Dissolve it in high-purity, deionized or distilled water (not tap water).
3. Transfer to a 1-liter volumetric flask and fill to the mark with water. Mix thoroughly.
4. The pH should be 4.01 at 25°C. It changes slightly with temperature (~ -0.0012 pH/°C).
---
2. pH 6.86 Buffer (Equimolar Phosphate Buffer)
This buffer uses two salts. The dihydrogen phosphate is available food-grade; the hydrogen phosphate might need sourcing from a chemical supplier as a food additive (E339).
· Food-Grade Ingredients:
· Monopotassium Phosphate (KH₂PO₄) - (E340) Common in food processing.
· Disodium Phosphate (Na₂HPO₄) - (E339) Also common. Using sodium instead of potassium salts is standard for this buffer.
· Formula & MW:
· KH₂PO₄ = 136.09 g/mol
· Na₂HPO₄ (anhydrous) = 141.96 g/mol. (Note: The more common form is the dihydrate, Na₂HPO₄·2H₂O, MW = 177.99 g/mol. Ensure you know which you have!)
Calculation for 1 Liter of 0.025M Equimolar Buffer:
· Both salts are at 0.025M concentration.
· Mass of KH₂PO₄: 0.025 mol × 136.09 g/mol = 3.402 g
· Mass of Na₂HPO₄ (Anhydrous): 0.025 mol × 141.96 g/mol = 3.549 g
· Mass of Na₂HPO₄·2H₂O (Dihydrate): 0.025 mol × 177.99 g/mol = 4.450 g
Preparation (using the more common dihydrate):
1. Weigh 3.402 g of monopotassium phosphate (KH₂PO₄).
2. Weigh 4.450 g of disodium phosphate dihydrate (Na₂HPO₄·2H₂O).
3. Dissolve both salts together in high-purity water.
4. Transfer to a 1-liter volumetric flask, fill to the mark, and mix. pH = 6.86 at 25°C.
---
3. pH 9.18 Buffer (Borax Buffer) - The Challenge
This is the most problematic. The classic buffer for pH ~9.2 is Sodium Tetraborate Decahydrate (Borax, Na₂B₄O₇·10H₂O).
· Issue: Borax's food-grade status is controversial and it is not approved as a food additive in many jurisdictions (e.g., EU, US). It is sometimes used as a washing aid but not for direct consumption.
Alternative Food-Grade Buffer for High pH: Bicarbonate/Carbonate Buffer
A 0.025M Sodium Bicarbonate / 0.025M Sodium Carbonate buffer gives a pH of approximately 9.91 at 25°C, not 9.18. To get to 9.18, we need to adjust the ratio.
· Food-Grade Ingredients:
· Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) - Baking soda.
· Sodium Carbonate (Na₂CO₃) - Soda ash, washing soda (can be made by heating baking soda at 170°C for 1 hour).
Calculation to Approximate pH 9.18:
Using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for the carbonate system (pKa2 = 10.33 at 25°C):
pH = pKa2 + log([CO₃²⁻]/[HCO₃⁻])
9.18 = 10.33 + log(R) where R = [CO₃²⁻]/[HCO₃⁻]
log(R) = 9.18 - 10.33 = -1.15
R = 10⁻¹·¹⁵ = 0.0708
This means the buffer needs a much higher proportion of bicarbonate. Let's make a 0.05M total carbonate buffer.
· Let [HCO₃⁻] = x, then [CO₃²⁻] = 0.0708x
· Total carbonate = x + 0.0708x = 0.05 M
· 1.0708x = 0.05 → x = 0.0467 M (HCO₃⁻)
· [CO₃²⁻] = 0.05 - 0.0467 = 0.0033 M
Masses for 1 Liter:
· NaHCO₃: 0.0467 mol × 84.01 g/mol = 3.923 g
· Na₂CO₃ (anhydrous): 0.
LiveSeafood, [1/14/26 10:12 PM]
0033 mol × 105.99 g/mol = 0.350 g
Preparation (Approximate pH 9.18 Buffer):
1. Dry your sodium bicarbonate in an oven (~100°C) for 30 minutes to remove moisture. Cool in a desiccator.
2. Weigh 3.92 g of dried sodium bicarbonate.
3. Weigh 0.35 g of anhydrous sodium carbonate.
4. Dissolve both in CO₂-free, high-purity water (boil and cool water to remove CO₂).
5. Transfer to a 1-liter volumetric flask, fill to the mark with the CO₂-free water, and mix without vigorous shaking to minimize CO₂ absorption.
6. VERIFY WITH A CALIBRATED METER. Expect some drift as the solution equilibrates with air.
---
o
https://i0.wp.com/randomnerdtutorials.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/DHT22_RaspberryPi_ESP8266.jpg?quality=100&strip=all&ssl=1
# [Nanopb](https://jpa.kapsi.fi/nanopb/)
# What is distilled water?
Distilled water is a highly purified form of water that has been stripped of almost all of its impurities,
including minerals, salts, and other organic and inorganic compounds. Through the process of distillation, water is boiled,
turned into steam, and then cooled and condensed back into a liquid state. This process leaves behind contaminants,
resulting in water that is essentially pure H₂O.
How is distilled water made?
The process of creating distilled water mimics the natural water cycle and involves these key steps:
Boiling: Tap water or spring water is heated in a boiler until it reaches its boiling point and transforms into steam.
Evaporation: As the water evaporates into steam, it leaves behind dissolved solids, such as salts, minerals (like calcium and magnesium), and other non-volatile contaminants.
Condensation: The steam is then channeled into a separate cooling system or condenser. As the steam cools, it reverts to its liquid form.
Collection: The resulting liquid, now distilled water, is collected in a clean, sterile container.
What is the difference between distilled and purified water?
While both are clean forms of drinking water, there is a key distinction:
Distilled Water: This is a type of purified water that is created through the specific process of distillation (boiling and condensing).
This process removes nearly all minerals and other impurities.
Purified Water: This is a broader category of water that has been treated to remove impurities. Purification methods can include distillation,
reverse osmosis, deionization, or carbon filtration. The key difference is that some purification methods may not remove all minerals as effectively as distillation.
For water to be labeled as "purified," it must meet certain standards of purity, but it is not necessarily mineral-free.
https://www.axilscientific.com/products/chemicals/biological-buffers/2x-laemmli-sample-buffer-ph-68-biotechnology-grade-p-buf-5240.html
# Modbus sensors
are industrial devices using the standard Modbus protocol for digital communication, allowing them to send accurate data (like temperature, humidity, pressure, air quality)
over networks (RS485, TCP) to controllers (PLCs, BMS) using simple, cost-effective cabling, enabling daisy-chaining up to 247 devices for efficient data exchange in automation systems,
unlike analog sensors that need separate wiring for each signal.
[modbus esphome -1](https://esphome.io/components/modbus_controller/)
[modbus esphome -2 ](https://esphome.io/components/modbus/)
[esphome yaml modbus](https://github.com/mortenx/modbustcp_wifi_esphome/tree/60959a6fdde990ced413398072f1628c7e513b23)
[esphome in python](https://github.com/esphome/esphome/tree/dev/esphome)
https://ioninja.com/downloads/archive/ioninja/ioninja-5.9.1/
https://www.segger.com/products/debug-probes/j-link/technology/about-real-time-transfer/
STC-3008 Dual Digital Temperature Controller Two Relay Output 12V 24V 220V Thermoregulator Thermostat Heater Cooler With Probe
STC-3008 Dual Relay Digital Thermostat Controller NTC Sensor 12V 24V 110V 220V Adjustable Heating Cooling Switch
STC-8080A+ Refrigeration Temperature Controller Digital Thermostat for Freezer Cold Storage Defrost Fridge Use
Refrigeration Temperature Controller STC 8080A with Cooling Defrost and Over Temperature Alarm for Freezer Cold Room
STC-9200A/EK-3030 Temperature Controller for Refrigeration and Defrost Fans
Stainless Steel Electric Heating Tube 220V High-Temperature Grill & Oven Heater Rod for BBQ and Industrial Equipment
220V Digital Temperature Controller EK-3010/EK-3020/EK-3030 Refrigerator Refrigeration Defrost Thermostat Sensor
Upgraded heating cable transparent floor heating wire 100m 12K 33 ohm / M carbon electric heating cable
5/10/20/25/50/200/500/1000ml Class A Borosilicate Glass Lab Clear Volumetric Flask With Head Stopper
Yieryi MH1230A AC220V Digital Temperature Controller Thermocouple -40 ~ 120 Degrees Thermostat Refrigeration Heating Regulator
pH 4
Potassium Citrate 2.63g
Citric acid monohydrate 3.45g
(if using anhydrous citric acid, use 3.15g)
pH 7
Potassium Citrate 7.14g
Citric acid monohydrate 0.35g
(if using anhydrous citric acid, use 0.32g)
Class A Volumetric Flask (250mL)
LiveSeafood, [1/14/26 10:12 PM]
Excellent question. Preparing precise pH buffers from food-grade ingredients is a common need in food science, home brewing, and artisanal fermentation labs. While "food-grade" limits the chemicals we can use, we can achieve good approximations.
Critical Note: Food-grade chemicals have lower purity (typically 97-99%) than lab-grade (>99.9%). This, along with variations in mineral content of water, will affect the absolute accuracy. For critical work, always verify the pH with a recently calibrated meter.
Here are the calculations and methods for the three buffers at 25°C.
---
1. pH 4.01 Buffer (Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate, 0.05M)
This is the most straightforward, as the primary ingredient is available as a pH standard in food-grade form.
· Food-Grade Ingredient: Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate (KHP). It's commonly used as an acidulant and stabilizer (E336).
· Formula: KHC₈H₄O₄
· Molecular Weight: 204.22 g/mol
Calculation for 1 Liter of 0.05M Solution:
Moles = Molarity × Volume = 0.05 mol/L × 1 L = 0.05 mol
Mass = Moles × Molecular Weight = 0.05 mol × 204.22 g/mol = 10.211 g
Preparation:
1. Weigh 10.21 grams of food-grade potassium hydrogen phthalate.
2. Dissolve it in high-purity, deionized or distilled water (not tap water).
3. Transfer to a 1-liter volumetric flask and fill to the mark with water. Mix thoroughly.
4. The pH should be 4.01 at 25°C. It changes slightly with temperature (~ -0.0012 pH/°C).
---
2. pH 6.86 Buffer (Equimolar Phosphate Buffer)
This buffer uses two salts. The dihydrogen phosphate is available food-grade; the hydrogen phosphate might need sourcing from a chemical supplier as a food additive (E339).
· Food-Grade Ingredients:
· Monopotassium Phosphate (KH₂PO₄) - (E340) Common in food processing.
· Disodium Phosphate (Na₂HPO₄) - (E339) Also common. Using sodium instead of potassium salts is standard for this buffer.
· Formula & MW:
· KH₂PO₄ = 136.09 g/mol
· Na₂HPO₄ (anhydrous) = 141.96 g/mol. (Note: The more common form is the dihydrate, Na₂HPO₄·2H₂O, MW = 177.99 g/mol. Ensure you know which you have!)
Calculation for 1 Liter of 0.025M Equimolar Buffer:
· Both salts are at 0.025M concentration.
· Mass of KH₂PO₄: 0.025 mol × 136.09 g/mol = 3.402 g
· Mass of Na₂HPO₄ (Anhydrous): 0.025 mol × 141.96 g/mol = 3.549 g
· Mass of Na₂HPO₄·2H₂O (Dihydrate): 0.025 mol × 177.99 g/mol = 4.450 g
Preparation (using the more common dihydrate):
1. Weigh 3.402 g of monopotassium phosphate (KH₂PO₄).
2. Weigh 4.450 g of disodium phosphate dihydrate (Na₂HPO₄·2H₂O).
3. Dissolve both salts together in high-purity water.
4. Transfer to a 1-liter volumetric flask, fill to the mark, and mix. pH = 6.86 at 25°C.
---
3. pH 9.18 Buffer (Borax Buffer) - The Challenge
This is the most problematic. The classic buffer for pH ~9.2 is Sodium Tetraborate Decahydrate (Borax, Na₂B₄O₇·10H₂O).
· Issue: Borax's food-grade status is controversial and it is not approved as a food additive in many jurisdictions (e.g., EU, US). It is sometimes used as a washing aid but not for direct consumption.
Alternative Food-Grade Buffer for High pH: Bicarbonate/Carbonate Buffer
A 0.025M Sodium Bicarbonate / 0.025M Sodium Carbonate buffer gives a pH of approximately 9.91 at 25°C, not 9.18. To get to 9.18, we need to adjust the ratio.
· Food-Grade Ingredients:
· Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) - Baking soda.
· Sodium Carbonate (Na₂CO₃) - Soda ash, washing soda (can be made by heating baking soda at 170°C for 1 hour).
Calculation to Approximate pH 9.18:
Using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for the carbonate system (pKa2 = 10.33 at 25°C):
pH = pKa2 + log([CO₃²⁻]/[HCO₃⁻])
9.18 = 10.33 + log(R) where R = [CO₃²⁻]/[HCO₃⁻]
log(R) = 9.18 - 10.33 = -1.15
R = 10⁻¹·¹⁵ = 0.0708
This means the buffer needs a much higher proportion of bicarbonate. Let's make a 0.05M total carbonate buffer.
· Let [HCO₃⁻] = x, then [CO₃²⁻] = 0.0708x
· Total carbonate = x + 0.0708x = 0.05 M
· 1.0708x = 0.05 → x = 0.0467 M (HCO₃⁻)
· [CO₃²⁻] = 0.05 - 0.0467 = 0.0033 M
Masses for 1 Liter:
· NaHCO₃: 0.0467 mol × 84.01 g/mol = 3.923 g
· Na₂CO₃ (anhydrous): 0.
LiveSeafood, [1/14/26 10:12 PM]
0033 mol × 105.99 g/mol = 0.350 g
Preparation (Approximate pH 9.18 Buffer):
1. Dry your sodium bicarbonate in an oven (~100°C) for 30 minutes to remove moisture. Cool in a desiccator.
2. Weigh 3.92 g of dried sodium bicarbonate.
3. Weigh 0.35 g of anhydrous sodium carbonate.
4. Dissolve both in CO₂-free, high-purity water (boil and cool water to remove CO₂).
5. Transfer to a 1-liter volumetric flask, fill to the mark with the CO₂-free water, and mix without vigorous shaking to minimize CO₂ absorption.
6. VERIFY WITH A CALIBRATED METER. Expect some drift as the solution equilibrates with air.
---
 Summary Table for 1L Buffer Solutions
Target pH Food-Grade Ingredients Quantities for 1L (at 25°C) Notes
4.01 Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate (KHP) 10.21 g Most accurate & reliable food-grade option.
6.86 Monopotassium Phosphate (KH₂PO₄) + Disodium Phosphate Dihydrate (Na₂HPO₄·2H₂O) 3.402 g + 4.450 g Standard phosphate buffer. Good stability.
~9.18 Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) + Sodium Carbonate (Na₂CO₃) 3.92 g + 0.35 g Approximation. Sensitive to CO₂. Verify pH.
General Preparation Protocol:
1. Use Precise Equipment: Analytical balance (0.01g min) and volumetric glassware.
2. Use Pure Water: Always use distilled or deionized water. For pH 9+ buffers, boil and cool it to remove CO₂.
3. Temperature: The pH of buffers is temperature-dependent. The values above are for 25°C. Allow solutions to reach room temperature before final verification.
4. Calibration: Calibrate your pH meter using commercial, traceable pH 4.01 and 7.00 buffers first. Then measure your prepared buffers.
5. Storage: Store in airtight, chemical-resistant bottles (HDPE or glass). Phosphate buffer is susceptible to microbial growth; refrigerate or make fresh frequently.
Disclaimer: These preparations are suitable for food science applications where trace impurities are acceptable. For regulatory compliance or absolute analytical precision,
certified buffer solutions or lab-grade chemicals are required.
[buffer solution for calibration](https://www.yokogawa.com/sg/solutions/products-and-services/measurement/analyzers/liquid-analyzers/ph-sensors/ph-orp-buffer-calibration-solutions-buffer-capsules/#Resources)
## [FDR (Frequency Domain Reflectometry)- soil](https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/domain-reflectometry)
https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005009437373461.html?spm=a2g0o.detail.pcDetailBottomMoreOtherSeller.2.37cajCwqjCwqUC&gps-id=pcDetailBottomMoreOtherSeller&scm=1007.40050.354490.0&scm_id=1007.40050.354490.0&scm-url=1007.40050.354490.0&pvid=abb75415-dc9d-4c38-8539-0b7fb4e38954&_t=gps-id:pcDetailBottomMoreOtherSeller,scm-url:1007.40050.354490.0,pvid:abb75415-dc9d-4c38-8539-0b7fb4e38954,tpp_buckets:668%232846%238116%232002&isseo=y&pdp_ext_f=%7B%22order%22%3A%2235%22%2C%22eval%22%3A%221%22%2C%22sceneId%22%3A%2230050%22%2C%22fromPage%22%3A%22recommend%22%7D&pdp_npi=6%40dis%21SGD%2131.09%2119.90%21%21%21163.52%21104.65%21%402102eaa317683497537194929e5259%2112000049099411629%21rec%21SG%21775789526%21X%211%210%21n_tag%3A-29919%3Bd%3Aaaab9621%3Bm03_new_user%3A-29895&utparam-url=scene%3ApcDetailBottomMoreOtherSeller%7Cquery_from%3A%7Cx_object_id%3A1005009437373461%7C_p_origin_prod%3A#nav-specification
https://zlj490490.en.made-in-china.com/
## [Modbus RTU](https://www.jxct-iot.com/product/showproduct.php?id=208)
Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) is the most widely used version of Modbus. It operates over serial communication lines like RS-485 or RS-232.
The RTU format includes a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for error checking,
ensuring reliable data transmission. It is particularly favored for its simplicity and robustness in harsh industrial environments.
```
#include "cpplinq.hpp"
using namespace cpplinq;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
int ints[] = {5,7,4,7,8,15,9,25,15,14,30,9,24,5,78,912,37,48,980,200,201};
int result = from_array(ints)
>> where([](int i) {return i%2 == 0;})
>> where([](int i) {return i < 100;})
>> max();
Serial.println(result);
}
void loop() {}
```
# Frequency Ranges for Moisture Meters
The frequency range used in moisture meters depends on the material being tested (soil, fertilizer, coal, etc.) and the measurement technique. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the typical MHz frequencies used and why they matter:
Common Frequency Ranges for Moisture Meters
Frequency Range Application Advantages Limitations
1–20 MHz Soil, Fertilizers, Coal, Powders - Balances penetration depth & sensitivity.
Summary Table for 1L Buffer Solutions
Target pH Food-Grade Ingredients Quantities for 1L (at 25°C) Notes
4.01 Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate (KHP) 10.21 g Most accurate & reliable food-grade option.
6.86 Monopotassium Phosphate (KH₂PO₄) + Disodium Phosphate Dihydrate (Na₂HPO₄·2H₂O) 3.402 g + 4.450 g Standard phosphate buffer. Good stability.
~9.18 Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) + Sodium Carbonate (Na₂CO₃) 3.92 g + 0.35 g Approximation. Sensitive to CO₂. Verify pH.
General Preparation Protocol:
1. Use Precise Equipment: Analytical balance (0.01g min) and volumetric glassware.
2. Use Pure Water: Always use distilled or deionized water. For pH 9+ buffers, boil and cool it to remove CO₂.
3. Temperature: The pH of buffers is temperature-dependent. The values above are for 25°C. Allow solutions to reach room temperature before final verification.
4. Calibration: Calibrate your pH meter using commercial, traceable pH 4.01 and 7.00 buffers first. Then measure your prepared buffers.
5. Storage: Store in airtight, chemical-resistant bottles (HDPE or glass). Phosphate buffer is susceptible to microbial growth; refrigerate or make fresh frequently.
Disclaimer: These preparations are suitable for food science applications where trace impurities are acceptable. For regulatory compliance or absolute analytical precision,
certified buffer solutions or lab-grade chemicals are required.
[buffer solution for calibration](https://www.yokogawa.com/sg/solutions/products-and-services/measurement/analyzers/liquid-analyzers/ph-sensors/ph-orp-buffer-calibration-solutions-buffer-capsules/#Resources)
## [FDR (Frequency Domain Reflectometry)- soil](https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/domain-reflectometry)
https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005009437373461.html?spm=a2g0o.detail.pcDetailBottomMoreOtherSeller.2.37cajCwqjCwqUC&gps-id=pcDetailBottomMoreOtherSeller&scm=1007.40050.354490.0&scm_id=1007.40050.354490.0&scm-url=1007.40050.354490.0&pvid=abb75415-dc9d-4c38-8539-0b7fb4e38954&_t=gps-id:pcDetailBottomMoreOtherSeller,scm-url:1007.40050.354490.0,pvid:abb75415-dc9d-4c38-8539-0b7fb4e38954,tpp_buckets:668%232846%238116%232002&isseo=y&pdp_ext_f=%7B%22order%22%3A%2235%22%2C%22eval%22%3A%221%22%2C%22sceneId%22%3A%2230050%22%2C%22fromPage%22%3A%22recommend%22%7D&pdp_npi=6%40dis%21SGD%2131.09%2119.90%21%21%21163.52%21104.65%21%402102eaa317683497537194929e5259%2112000049099411629%21rec%21SG%21775789526%21X%211%210%21n_tag%3A-29919%3Bd%3Aaaab9621%3Bm03_new_user%3A-29895&utparam-url=scene%3ApcDetailBottomMoreOtherSeller%7Cquery_from%3A%7Cx_object_id%3A1005009437373461%7C_p_origin_prod%3A#nav-specification
https://zlj490490.en.made-in-china.com/
## [Modbus RTU](https://www.jxct-iot.com/product/showproduct.php?id=208)
Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) is the most widely used version of Modbus. It operates over serial communication lines like RS-485 or RS-232.
The RTU format includes a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for error checking,
ensuring reliable data transmission. It is particularly favored for its simplicity and robustness in harsh industrial environments.
```
#include "cpplinq.hpp"
using namespace cpplinq;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
int ints[] = {5,7,4,7,8,15,9,25,15,14,30,9,24,5,78,912,37,48,980,200,201};
int result = from_array(ints)
>> where([](int i) {return i%2 == 0;})
>> where([](int i) {return i < 100;})
>> max();
Serial.println(result);
}
void loop() {}
```
# Frequency Ranges for Moisture Meters
The frequency range used in moisture meters depends on the material being tested (soil, fertilizer, coal, etc.) and the measurement technique. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the typical MHz frequencies used and why they matter:
Common Frequency Ranges for Moisture Meters
Frequency Range Application Advantages Limitations
1–20 MHz Soil, Fertilizers, Coal, Powders - Balances penetration depth & sensitivity.- Minimizes ionic conductivity effects. - May still be affected by high salt content. 50–150 MHz High-Precision Agriculture, Industrial Materials - Better resolution for low-moisture materials.
- Less affected by density variations. - More expensive hardware. 200–1000 MHz (GHz range) Lab-Grade Analysis, Pharmaceuticals - Detects bound vs. free water.
- Works with very fine powders. - Limited field use due to complexity. Why These Frequencies? 1–20 MHz (Most Common for Portable Meters) Optimal for granular materials (soil, sand, fertilizer). Low enough to avoid excessive signal loss in conductive materials (e.g., salty soils). High enough to ignore electrode polarization errors (common in low-frequency meters). 50–150 MHz (Advanced Industrial Use) Used in precision agriculture and process control (e.g., coal moisture in power plants). Better for low-moisture powders (e.g., dry chemicals, cement). 200+ MHz (Research & Lab Instruments) Detects different water states (free vs. bound water). Used in pharmaceuticals and food science where exact moisture is critical. Key Considerations When Choosing a Frequency Material Type: Soil/Fertilizer: 5–50 MHz (avoids salt interference). Coal/Powders: 10–100 MHz (density-independent). Chemical Powders: 20–200 MHz (fine particles need higher frequencies). Moisture Range: High moisture (>20%) → Lower MHz (1–20 MHz). Low moisture (<5%) → Higher MHz (50+ MHz). Conductivity Effects: If the material is salty or conductive (e.g., some fertilizers), higher frequencies (50+ MHz) reduce errors. Best Practices for Moisture Measurement ✔ Use a meter with adjustable frequency if working with multiple materials. ✔ Calibrate for each material (fertilizer vs. coal vs. soil). ✔ Avoid very low frequencies (<1 MHz) if measuring conductive materials. Would you like recommendations for specific moisture meters based on your application? # [esp32](https://rust-dd.com/post/introduction-to-embedded-systems-with-rust-a-beginner-s-guide-using-esp32) - [esp-dsp module](https://github.com/espressif/esp-dsp/blob/master/examples/basic_math/main/dsps_math_main.c) - [Custom display](https://blog.embeddedexpert.io/?p=27650) or EEZ Studio,Squareline studio - generate cpp code LVGL - [include TFT_eSPI library](https://www.digikey.tw/zh/maker/projects/elecrow-crow-panel-2.8-esp32-hmi-display-simple-tft_espi-examples/e54c6083ba8a41ebb3da7c4efd33444e) - [FreeRTOS esp32](https://medium.com/@tomw3115/implementing-freertos-solutions-on-esp-32-devices-using-arduino-fa64c5d88605) - [free rtos esp32 and adriono](https://wolles-elektronikkiste.de/en/using-freertos-with-esp32-and-arduino) - [realtime kernel](https://homel.vsb.cz/~sta048/mcu/doc/freertos/Mastering-the-FreeRTOS-Real-Time-Kernel.v1.0.pdf) - [ESPHOME Aqqua](https://github.com/TheRealFalseReality/aquapi?tab=readme-ov-file) -
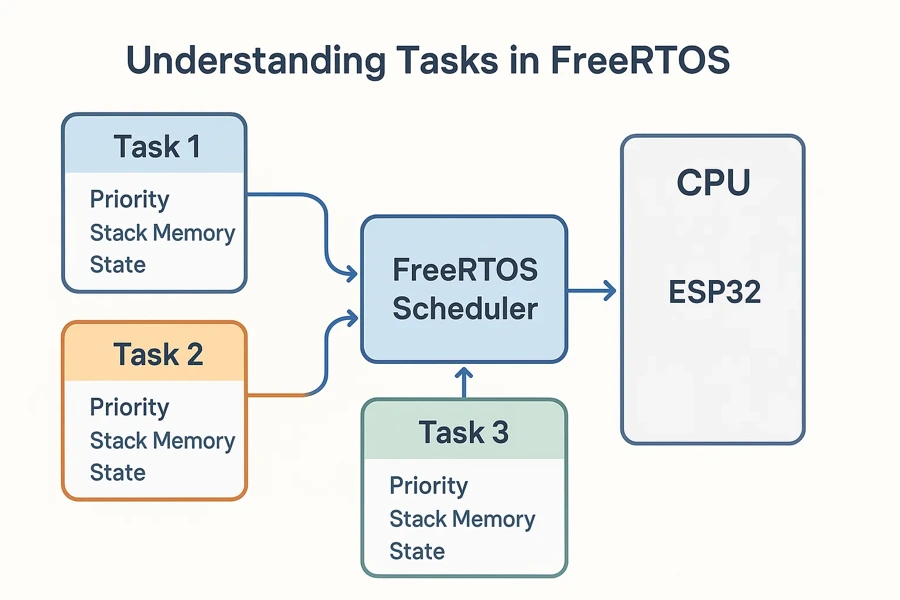 -
- 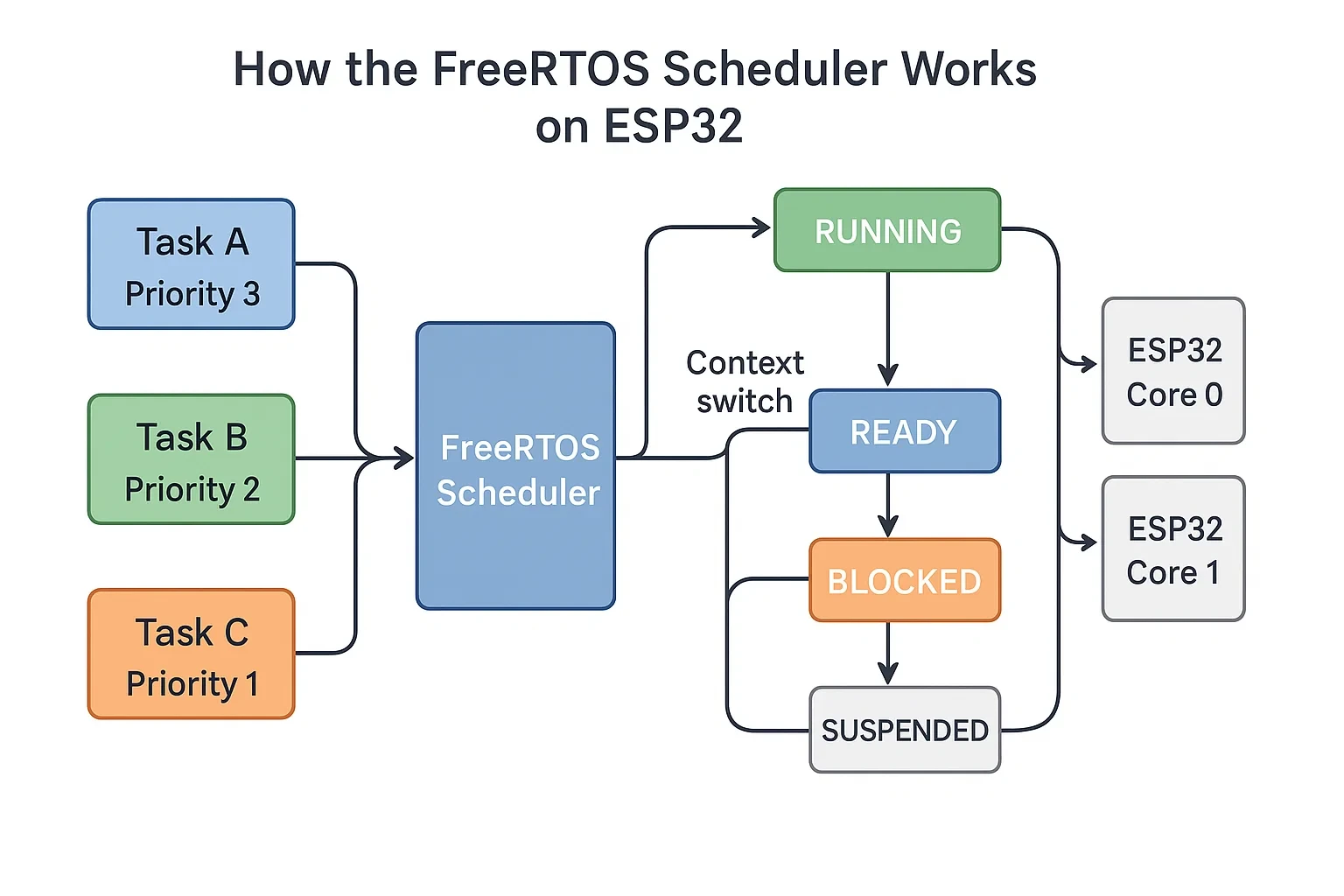 -
-  -
-  -
-  - [freeRTOS univertisty wisconsin](https://ece353.engr.wisc.edu/freertos/queues/)
- Double buffer instead of circular Buffer
-
- [freeRTOS univertisty wisconsin](https://ece353.engr.wisc.edu/freertos/queues/)
- Double buffer instead of circular Buffer
-  -
-  -
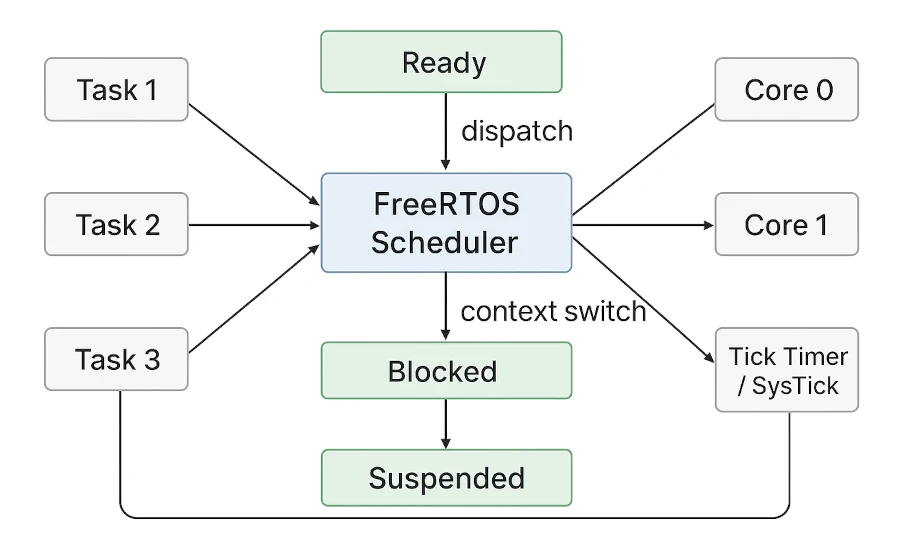
-  - Memory allocation in freertos
When FreeRTOS requires RAM it calls pvPortMalloc() instead of malloc(). Likewise, when FreeRTOS frees previously allocated RAM it calls vPortFree() instead of free().
pvPortMalloc() has the same prototype as the standard C library malloc() function, and vPortFree() has the same prototype as the standard C library free() function.
pvPortMalloc() and vPortFree() are public functions, so can also be called from application code.
FreeRTOS comes with five example implementations of pvPortMalloc() and vPortFree(), which
# [Step 4: Build and Flash the Project](https://www.oceanlabz.in/dynamic-memory-allocation-in-freertos/?srsltid=AfmBOortTOiF-1ePjg2wiFSQ2I-NKGJgnLPjlcBVZCTqRGQMaCMCrjhi)
- . :/media/edy/LocakDsk/Arduino/esp-idf/export.sh
- idf.py build
- idf.py -p /dev/ttyACM0 flash
- idf.py monitor
# waiting for interrupt
void vApplicationIdleHook( void )
{
asm volatile (" WFI \n" );
}
# [Micropythn esp32c6](https://micropython.org/download/ESP32_GENERIC_C6/)
- cargo install espup
- [spotpear](https://spotpear.com/wiki/ESP32-C6-LCD-1.47-inch-LCD-Display-TouchScreen-LVGL-SD-AXS5106L-JD9853.html)
# [Three phase PWM](https://blog.embeddedexpert.io/?p=3920)
# [1 wire protocol using 9600bps?](https://blog.embeddedexpert.io/?p=3896)
- [more detail](https://blog.embeddedexpert.io/?p=3858)
- use software instead of hardware for daata write and read (master slave configuration)
|Material |p (RESISIVITY) IN OHM-CM|
|---------|------------------------|
|Aluminium| 2.82 × 10-6
|Copper | 1.68 × 10%6
|Gold |2.44 × 10-6
|Iron |1.00 x 10-5
|Silver |1.59 × 10-6|
# Vn Dorn Bottle ( collect water sample with depth)
# salinity refractometer
a salinity refractometer is generally more accurate than a conductivity-based salinity probe for measuring salinity in aqueous solutions, particularly in marine and aquarium applications. Here’s why:
1. Principle of Measurement
Refractometer: Measures salinity based on the refractive index of water, which changes with dissolved salts. This method directly correlates with the actual salt content.
Conductivity Probe: Measures salinity indirectly by detecting electrical conductivity, which depends on ion concentration. However, conductivity can be affected by factors other than salinity (e.g., temperature, dissolved organics, or other ions).
2. Accuracy & Precision
Refractometers provide higher precision (±0.1–0.2 ppt) for salinity measurements in seawater and brines.
Conductivity probes can be less precise (±1–2 ppt or more) unless calibrated frequently and compensated for temperature.
3. Common Interferences
Refractometer: Mostly unaffected by non-salt impurities (e.g., organics, gases) unless they significantly alter refractive index.
Conductivity Probe: Affected by temperature fluctuations, contaminants (e.g., ammonia, CO₂), and non-salt ions, leading to potential inaccuracies.
4. Calibration & Maintenance
Refractometers require simple calibration with distilled water or a known standard.
Conductivity probes need regular calibration (often with standard solutions) and temperature compensation for accurate readings.
When to Use Each?
Use a refractometer for:
Marine aquariums (reef tanks, saltwater systems)
Brine solutions (food processing, hydroponics)
High-precision salinity checks
Use a conductivity probe for:
Continuous monitoring (e.g., aquaculture, industrial processes)
Situations where rapid, automated readings are needed
Conclusion
For absolute salinity accuracy, a refractometer is superior. However, conductivity probes are useful for real-time monitoring where slight variations are acceptable. For critical applications (e.g., coral reef tanks), a refractometer is the gold standard.
Final Tips for Best Results
✅ For refractometers:
Store in a protective case (prevents scratches).
Avoid direct sunlight (can warp the prism).
✅ For conductivity probes:
Use storage solution (like KCl) to prolong lifespan.
Replace every 1–2 years for consistent accuracy.
# Prevent Fouling for conductivity probe
- Memory allocation in freertos
When FreeRTOS requires RAM it calls pvPortMalloc() instead of malloc(). Likewise, when FreeRTOS frees previously allocated RAM it calls vPortFree() instead of free().
pvPortMalloc() has the same prototype as the standard C library malloc() function, and vPortFree() has the same prototype as the standard C library free() function.
pvPortMalloc() and vPortFree() are public functions, so can also be called from application code.
FreeRTOS comes with five example implementations of pvPortMalloc() and vPortFree(), which
# [Step 4: Build and Flash the Project](https://www.oceanlabz.in/dynamic-memory-allocation-in-freertos/?srsltid=AfmBOortTOiF-1ePjg2wiFSQ2I-NKGJgnLPjlcBVZCTqRGQMaCMCrjhi)
- . :/media/edy/LocakDsk/Arduino/esp-idf/export.sh
- idf.py build
- idf.py -p /dev/ttyACM0 flash
- idf.py monitor
# waiting for interrupt
void vApplicationIdleHook( void )
{
asm volatile (" WFI \n" );
}
# [Micropythn esp32c6](https://micropython.org/download/ESP32_GENERIC_C6/)
- cargo install espup
- [spotpear](https://spotpear.com/wiki/ESP32-C6-LCD-1.47-inch-LCD-Display-TouchScreen-LVGL-SD-AXS5106L-JD9853.html)
# [Three phase PWM](https://blog.embeddedexpert.io/?p=3920)
# [1 wire protocol using 9600bps?](https://blog.embeddedexpert.io/?p=3896)
- [more detail](https://blog.embeddedexpert.io/?p=3858)
- use software instead of hardware for daata write and read (master slave configuration)
|Material |p (RESISIVITY) IN OHM-CM|
|---------|------------------------|
|Aluminium| 2.82 × 10-6
|Copper | 1.68 × 10%6
|Gold |2.44 × 10-6
|Iron |1.00 x 10-5
|Silver |1.59 × 10-6|
# Vn Dorn Bottle ( collect water sample with depth)
# salinity refractometer
a salinity refractometer is generally more accurate than a conductivity-based salinity probe for measuring salinity in aqueous solutions, particularly in marine and aquarium applications. Here’s why:
1. Principle of Measurement
Refractometer: Measures salinity based on the refractive index of water, which changes with dissolved salts. This method directly correlates with the actual salt content.
Conductivity Probe: Measures salinity indirectly by detecting electrical conductivity, which depends on ion concentration. However, conductivity can be affected by factors other than salinity (e.g., temperature, dissolved organics, or other ions).
2. Accuracy & Precision
Refractometers provide higher precision (±0.1–0.2 ppt) for salinity measurements in seawater and brines.
Conductivity probes can be less precise (±1–2 ppt or more) unless calibrated frequently and compensated for temperature.
3. Common Interferences
Refractometer: Mostly unaffected by non-salt impurities (e.g., organics, gases) unless they significantly alter refractive index.
Conductivity Probe: Affected by temperature fluctuations, contaminants (e.g., ammonia, CO₂), and non-salt ions, leading to potential inaccuracies.
4. Calibration & Maintenance
Refractometers require simple calibration with distilled water or a known standard.
Conductivity probes need regular calibration (often with standard solutions) and temperature compensation for accurate readings.
When to Use Each?
Use a refractometer for:
Marine aquariums (reef tanks, saltwater systems)
Brine solutions (food processing, hydroponics)
High-precision salinity checks
Use a conductivity probe for:
Continuous monitoring (e.g., aquaculture, industrial processes)
Situations where rapid, automated readings are needed
Conclusion
For absolute salinity accuracy, a refractometer is superior. However, conductivity probes are useful for real-time monitoring where slight variations are acceptable. For critical applications (e.g., coral reef tanks), a refractometer is the gold standard.
Final Tips for Best Results
✅ For refractometers:
Store in a protective case (prevents scratches).
Avoid direct sunlight (can warp the prism).
✅ For conductivity probes:
Use storage solution (like KCl) to prolong lifespan.
Replace every 1–2 years for consistent accuracy.
# Prevent Fouling for conductivity probe


 a salinometer based on the electrical conductivity of seawater, together with temperature, provides salinity (S) readings.
To be more specific, S is calculated from the ratio of the conductivity of seawater to that of a KCl solution (32.4356 g/kg), with both measurements made at 15 °C
and under one-atmosphere pressure [7,35,36,37]. It can then be converted to chlorinity using the Knudsen equation (Equation (1)) [6].
S (g Kg−1)=1.80665 Cl (g Kg−1)
- [seawater calculation on TEOS-10](https://monrecifamoi.saulme.fr/salinite/sea_water_calculator_teos10.php)
- [salinity on PS-788 formula](https://salinometry.com/pss-78/)
# [Temperature T90](https://www.fluke.com/en-us/learn/blog/calibration/its-90?srsltid=AfmBOoohzT0IVs5LWmdxRaTlXLjq-iJ-acMKxxWhLNSr8dyFQ98EE7rf)
# install uv in windows
winget install --id=astral-sh.uv -e
uv self update
uv python install 3.14
uv add flask
uv run -- flask run -p 3000
Create a project.
uv init project
Move into the project directory.
cd project
Add ipykernel as a dev dependency.
uv add --dev ipykernel
Open the project in VS Code.
code .
8. Case Study: OpenCTD Anti-Fouling
The open-source OpenCTD uses:
Teflon-coated electrodes.
Pulsed AC measurement (no DC bias).
Manual cleaning during calibration.
. Effectiveness Comparison
|Method| Biofilm Prevention| Mineral Fouling |Cost| Complexity|
|------|-------------------------|----------------------|----|------------|
|Silicone Coatings| Medium |Low |$| Low|
|Mechanical Wipers| High| High| $$$ High|
|Pulsed Polarization| Medium| Medium| $$| Medium|
|UV-C LEDs| High| Low| $$ |Medium|
[Howland current pump using voltage opamp](https://neurophysics.ucsd.edu/courses/physics_171/The%20Howland%20Current%20Pump.pdf)
[show constant current](https://circuitcellar.com/resources/quickbits/howland-current-source/)
[Design guide](https://www.how2power.com/search/index.php)
[Image Maker](https://imageresizer.com/)
[pdfum binary](https://github.com/bblanchon/pdfium-binaries)
# [Fisherman boat](https://explorer.com.my/product/e190-floorboard/)
## Perahu fiber lebih dangkal karena ringgang untuk pulau yang berkarang karena karang bisa membuat perahu itu pecah/rusak
- fiber perahu ika dari malaysia (40HP=40PK- 54juta)-need 15PK (15PK=32 juta)
- Bor air : 12 m air laut, 30m air tawar
- di palemenbang 120m dapat air minum
- kaporit terlalu tinggi di danau di atas petong
- cumi yang di es berwarna merah keesokan harinya
- 1 knot =1.852km/hours
- [fisherman boats](https://jixingxincomposite.en.made-in-china.com/product/NJpUiKoPaQYS/China-New-Design-High-Quality-Motor-Boat-Boat-Fishing-Fiberglass-Boat.html)
- inyak 40pk motor (oil consumption 20L/hours)
- Water coloumn
- air laut bataam diambil dari kedalaman 12m, di Norwegia diambil dari kedalamaan 75m dari permukaan laut
- fiber boat puny hendra pulaupetong:
-17" dan 21" (5.5 m ~ 7 m) , boat: 27 juta
- mesin yamaha 15HP ( 2x)
- supaya temperature nya hampir sama dengan culture temperature
- Pulau Benan: Judit, Petong Hendra
- pH nya konstant di kedalaman ?
- [cuaca dan agin di pulau petong](https://www.windy.com/0.629/104.082?0.626,104.094,15)
- 65% kapal nelayan adalaah terbuat dari kayu (10`15 year)
- Mesin bukan dmeesia kapal akibatnya mudah terjadi korosi
* [Clasification River class boat](https://itayachtscanada.com/understand-the-class-a-b-c-d-in-yachting/)
* [First aid in the boat](https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-46/chapter-I/subchapter-W/part-199/subpart-B/section-199.175)
# Boat engine
- Yamaha, Suzuki, Honda
- Yamabisi (9.9 HP, 7.3kW) - speed 10km/hour
- fuel pump
- 92 octane
- 4 stroke
- Mercury
- China outboard engines (gasoline?, electric):
- Parsun
-
- shallow water
- need long tail engine
## Two engine on the back
- mounting on the opposite direction for engine one and engine two . ( only the fance of the engine ?)
- higher drag for 2 engine
- Engine running at 1000rmpm, 3000rmp (fuel economy), 4000rmpm, 5000rpm and 5800 rpm (max)
- Smaller engine can be all electric
- Hangkian marine egine (electric)
## [Hull speed](https://www.marineinsight.com/marine-navigation/understanding-vessels-hull-speed-and-its-determination/)
- it is posible to incrase boat speed to > hull speed with various method
## [Longtail boat Thailand](https://snorkelingthailand.com/thai-longtail-boat/)
[longtail 2](https://www.mdpi.com/2032-6653/12/1/36)
## Buble help ship save fuel
[Hull calculator](https://www.omnicalculator.com/sports/hull-speed)
|Water line length
a salinometer based on the electrical conductivity of seawater, together with temperature, provides salinity (S) readings.
To be more specific, S is calculated from the ratio of the conductivity of seawater to that of a KCl solution (32.4356 g/kg), with both measurements made at 15 °C
and under one-atmosphere pressure [7,35,36,37]. It can then be converted to chlorinity using the Knudsen equation (Equation (1)) [6].
S (g Kg−1)=1.80665 Cl (g Kg−1)
- [seawater calculation on TEOS-10](https://monrecifamoi.saulme.fr/salinite/sea_water_calculator_teos10.php)
- [salinity on PS-788 formula](https://salinometry.com/pss-78/)
# [Temperature T90](https://www.fluke.com/en-us/learn/blog/calibration/its-90?srsltid=AfmBOoohzT0IVs5LWmdxRaTlXLjq-iJ-acMKxxWhLNSr8dyFQ98EE7rf)
# install uv in windows
winget install --id=astral-sh.uv -e
uv self update
uv python install 3.14
uv add flask
uv run -- flask run -p 3000
Create a project.
uv init project
Move into the project directory.
cd project
Add ipykernel as a dev dependency.
uv add --dev ipykernel
Open the project in VS Code.
code .
8. Case Study: OpenCTD Anti-Fouling
The open-source OpenCTD uses:
Teflon-coated electrodes.
Pulsed AC measurement (no DC bias).
Manual cleaning during calibration.
. Effectiveness Comparison
|Method| Biofilm Prevention| Mineral Fouling |Cost| Complexity|
|------|-------------------------|----------------------|----|------------|
|Silicone Coatings| Medium |Low |$| Low|
|Mechanical Wipers| High| High| $$$ High|
|Pulsed Polarization| Medium| Medium| $$| Medium|
|UV-C LEDs| High| Low| $$ |Medium|
[Howland current pump using voltage opamp](https://neurophysics.ucsd.edu/courses/physics_171/The%20Howland%20Current%20Pump.pdf)
[show constant current](https://circuitcellar.com/resources/quickbits/howland-current-source/)
[Design guide](https://www.how2power.com/search/index.php)
[Image Maker](https://imageresizer.com/)
[pdfum binary](https://github.com/bblanchon/pdfium-binaries)
# [Fisherman boat](https://explorer.com.my/product/e190-floorboard/)
## Perahu fiber lebih dangkal karena ringgang untuk pulau yang berkarang karena karang bisa membuat perahu itu pecah/rusak
- fiber perahu ika dari malaysia (40HP=40PK- 54juta)-need 15PK (15PK=32 juta)
- Bor air : 12 m air laut, 30m air tawar
- di palemenbang 120m dapat air minum
- kaporit terlalu tinggi di danau di atas petong
- cumi yang di es berwarna merah keesokan harinya
- 1 knot =1.852km/hours
- [fisherman boats](https://jixingxincomposite.en.made-in-china.com/product/NJpUiKoPaQYS/China-New-Design-High-Quality-Motor-Boat-Boat-Fishing-Fiberglass-Boat.html)
- inyak 40pk motor (oil consumption 20L/hours)
- Water coloumn
- air laut bataam diambil dari kedalaman 12m, di Norwegia diambil dari kedalamaan 75m dari permukaan laut
- fiber boat puny hendra pulaupetong:
-17" dan 21" (5.5 m ~ 7 m) , boat: 27 juta
- mesin yamaha 15HP ( 2x)
- supaya temperature nya hampir sama dengan culture temperature
- Pulau Benan: Judit, Petong Hendra
- pH nya konstant di kedalaman ?
- [cuaca dan agin di pulau petong](https://www.windy.com/0.629/104.082?0.626,104.094,15)
- 65% kapal nelayan adalaah terbuat dari kayu (10`15 year)
- Mesin bukan dmeesia kapal akibatnya mudah terjadi korosi
* [Clasification River class boat](https://itayachtscanada.com/understand-the-class-a-b-c-d-in-yachting/)
* [First aid in the boat](https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-46/chapter-I/subchapter-W/part-199/subpart-B/section-199.175)
# Boat engine
- Yamaha, Suzuki, Honda
- Yamabisi (9.9 HP, 7.3kW) - speed 10km/hour
- fuel pump
- 92 octane
- 4 stroke
- Mercury
- China outboard engines (gasoline?, electric):
- Parsun
-
- shallow water
- need long tail engine
## Two engine on the back
- mounting on the opposite direction for engine one and engine two . ( only the fance of the engine ?)
- higher drag for 2 engine
- Engine running at 1000rmpm, 3000rmp (fuel economy), 4000rmpm, 5000rpm and 5800 rpm (max)
- Smaller engine can be all electric
- Hangkian marine egine (electric)
## [Hull speed](https://www.marineinsight.com/marine-navigation/understanding-vessels-hull-speed-and-its-determination/)
- it is posible to incrase boat speed to > hull speed with various method
## [Longtail boat Thailand](https://snorkelingthailand.com/thai-longtail-boat/)
[longtail 2](https://www.mdpi.com/2032-6653/12/1/36)
## Buble help ship save fuel
[Hull calculator](https://www.omnicalculator.com/sports/hull-speed)
|Water line length in feet |Hull speed
in knots| Hull speed
in mph |Hull speed
in km/h| |--------------------------|-------------------|--------------------|-----------------| |8 ft (2.438m) |3.8 kn |4.4 mph |7.0 km/h | |9 (2.74m) |4.0 |4.7 |7.4 | |10 (3.048m) |4.3 |4.9 |8.0 | |11|4.5|5.2|8.3| |12|4.7|5.4|8.7| |13|4.9|5.6|9.1| |14|5.0|5.8|9.3| |15 (4.57m)|5.2|6.0|9.6| |16|5.4|6.2|10.0| |17|5.6|6.4|10.3| |18|5.7|6.6|10.5| |19|5.9|6.8|10.9| |20|6.0 |6.9 |11.1| |21|6.2|7.1|11.5| |22|6.3|7.3|11.7| |23|6.5|7.5|12.0| |24|6.6|7.6|12.2| |25|6.7|7.8|12.4| |26|6.9|7.9|12.8| |27|7.0|8.1|13.0| |28|7.1|8.2|13.2| |29|7.3|8.4|13.5| |30|7.4|8.5|13.7| |31|7.5|8.6|13.9| # Anchovies process - [Anchovies(江鱼仔) process](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rHYgoOvGNXg) - [ikan Bilis (Teri) Malaysia](wwww.ikannbilis.com.my) - Purse seine # [Gyro stablizer](https://www.gineicomarine.com.au/how-does-a-gyro-stabiliser-work/) [product stablizer list](https://www.zhoujiatech.com/product_list/1.html?gad_source=1&gad_campaignid=21732637351&gclid=EAIaIQobChMI6JDG79vZjQMV8qRmAh1fLhEvEAAYASAAEgIstfD_BwE) ## [tauri](https://tauri.app/start/prerequisites/#linux) -[1](https://dioxuslabs.com/learn/0.6/guide/) -[2](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/79425798/how-do-i-build-a-dioxus-bare-bones-project-in-nix) -[dioxus lab](https://dioxuslabs.com/awesome/) # [Fly-by-Wire (FBW)](https://www.aviation-accidents.net/fly-by-wire-airplanes/) Fly-by-wire (FBW) cars utilize electronic systems instead of mechanical linkages to control driving functions. This technology, similar to FBW in aviation, replaces traditional steering columns and pedals with electronic controls. FBW allows for a more precise and potentially autonomous driving experience by eliminating the need for direct physical connections between the driver's input and the vehicle's actions. in a "fly-by-wire" (FBW) boat system, steering and throttle controls are not directly connected to the engine or rudder mechanism with cables or rods. Instead, a computer receives inputs from the steering wheel or joystick, processes them, and then sends electrical signals to actuators that control the boat's movement. This technology replaces traditional mechanical linkages with electronic systems, offering advantages like reduced weight, improved control, and potential for enhanced stability and automation Fly-by-wire (FBW) is a flight control system that replaces the mechanical linkages between the pilot’s control inputs and the aircraft’s control surfaces with electronic signals. In an FBW system, the pilot’s control inputs are detected by sensors and transmitted to a computer system, which then calculates the appropriate response and sends signals to actuators that move the control surfaces. [Fly-by-wire (FBW)](http://www2.coe.pku.edu.cn/tpic/20119195714364.pdf) is a system that replaces the conventional manual flight controls of an aircraft with an electronic interface. The movements of flight controls are converted to electronic signals transmitted by wires (hence the fly-by-wire term), and flight control computers determine how to move the actuators at each control surface to provide the ordered response. The fly-by-wire system also allows automatic signals sent by the aircraft's computers to perform functions without the pilot's input, as in systems that automatically help stabilize the aircraft. # perlu kapal 40HP untuk perairan dengan laut lepas (tanjung pinang) # [marketing fish](https://indofishmart.id) https://indofishmart.id/kerapu-cantang-hybrida-kerapu-yang-diminati-di-tiongkok-peluang-besar-untuk-ekspor-laut-indonesia/ - [Hatchery pemijahan](https://repository.ub.ac.id/id/eprint/135643/2/PKL.pdf) - [Journal perikanan](https://journal.asrihindo.or.id/index.php/Manfish/index) - [Journal kerapu cantang](https://journal.umg.ac.id/index.php/jpp/article/view/7239/4041) - [benih kerapu cantang](https://www.sikumis.com/produk/benih-kerapu-hybrid-cantang-macan-x-kertang-8-cm) Hibridisasi dilakukan dengan metode pembuahan buatan (artificial fertilization). **Kelamin kedua induk diurut agar telur dan sperma keluar melalui saluran kelaminnya. Setelah itu, telur dan sperma dicampurkan secara merata di dalam wadah baskom.** * Fertelization rate is 50% * Hatching rate hibrida larger than 50%. **Bagian penting dari hibridisasi ini adalah pengambilan sperma pada induk kerapu kertang jantan.** Sperma yang diambil tidak boleh sampai tercampur dengan air laut ataupun kotoran dari induk, pasalnya keduanya dapat menurunkan motilitas sperma sehingga tingkat pembuahan akan menurun. Telur kerapu hibrida akan menetas setelah 20 jam pembuahan. Panjang larva kerapu hibrida sekitar 1,6–1,8 mm. pakan larva kerapu # udang rebon (Mesopodopsis sp.) * Udang rebon adalah salah satu jenis udang air laut yang memiliki nilai ekonomi tinggi dan banyak dimanfaatkan sebagai bahan baku pembuatan terasi, serta menjadi objek penelitian dalam bidang ilmu kelautan dan biologi Chlorella sp. Chlorella sp. diberikan saat hari ketiga penebaran telur. Pemberian Chlorella sp. dengan cara dialirkan dari bak kultur Chlorella sp. ke bak pemeliharaan larva. Kultur Chlorella sp. diawali dengan mengisi bak kultur dengan air laut hingga mencapai volume 50% dari volume total. Selanjutnya, diisi bibit Chlorella sp. sebanyak 30% dari volume total bak. Pupuk urea 70 ppm, ZA 40 ppm dan TSP 38 ppm diberikan untuk menambah nutrisi dan meningkatkan pertumbuhan Chlorella sp. yang dikultur. Setiap unsur hara mempunyai fungsi khusus pada pertumbuhan dan kepadatan pakan alami. Dosis pemupukan yang tepat dan cara yang baik adalah salah satu faktor penting dalam proses kultur pakan alami. Chlorella sp. dapat dipanen setelah 5 hari kultur Rotifera sp. Rotifera sp. digunakan untuk larva berumur 3 hari (D3) sampai larva berumur 40 hari (D40). Pemberian Rotifera sp. dilakukan dengan cara ditebar dengan perlahan pada bak pemeliharaan larva. Pemberian Rotifera sp. sebanyak 3x, yaitu pukul 08.00, 09.00 dan 10.00 WIB. Pemberian Rotifera sp. diberikan dengan dosis 10 ind/ml. Letak bak Chlorella sp. dan bak Rotifera sp. harus berjauhan. Hal ini bertujuan untuk mencegah kontaminasi dan mencegah peralihan organisme pakan alami yang dikultur. Hal ini sesuai dengan pendapat Rahmaningsih dan Ari (2013), bahwa penempatan lokasi bak kultur Rotifera sp. harus dijauhkan dari bak kultur Chlorella sp., karena dapat mengakibatkan habisnya Chlorella yang termakan oleh Rotifera. Cara mengkultur Rotifera yaitu dengan cara menambhakan air laut sebanyak 5 ton, dan dicampurkan dengan 5 ton Chlorella, dan 3 ton bibit Rotifera. Setelah 2 hari Rotifera dapat dipanen. Artemia sp. Sebelum diberikan kepada larva, Artemia harus ditetaskan terlebih dahulu. Cara penetasan yang dilakukan di CV. SBB 88 dibagi menjadi 2 tahapan, yaitu dekapsulasi dan penetasan cyste artemia. Dekapsulasi dilakukan dengan cara menyiapkan cyste artemia dan diletakkan dalam timba yang bervolume 12liter. Setelah itu diberikan klorin sebanyak 500 ml dan diaduk menggunakan pipa panjang serta didiamkan selama 1 jam. Selanjutnya, diaduk hingga berubah warna dari yang awalnya coklat tua menjadi coklat muda. Setelah itu cyste artemia disaring menggunakan seser dan dicuci menggunakan air tawar. Cyste artemia disimpan di dalam kulkas sebelum ditetaskan. Penetasan artemia menggunakan timba bervolume 50liter yang sudah diisi air laut dan aerasi. Cyste artemia yang sudah didekapsulasi ditetaskan pada wadah tersebut sebanyak 50gram dan diaerasi dengan kekuatan tinggi. Proses penetasan Artemia membutuhkan waktu selama 10-12 jam. Pemberian artemia yang dilakukan di CV. SBB 88 adalah setelah larva berumur 15 hari (D15) sampai larva berumur 40 hari (D40). Pemberian pakan alami berupa Artemia dilakukan dalam 3 kali yakni pada jam 08.00, 10.00, dan 14.00 WIB. Setiap pemberian pakan berupa Artemia, dapat dihitung kepadatannya mencapai 10 ind/ml. Pemberian udang rebon Pakan udang rebon diberikan pada saat larva berumur 26 hari (D26), dengan dosis pemberian adlibitum. Dilakukan sebanyak dua kali sehari pukul 09.00 dan 11.00 WIB setelah pemberian Artemia.
 The conversion factor between these units is approximately:1 °dH (dGH) = 17.9 mg/L (ppm) as CaCO₃
Given a GH of 300 mg/L (which is also 300 ppm), the conversion is as follows: GH in mg/L (as CaCO₃):300 mg/L (or 300 ppm)
GH in degrees German Hardness (°dH or dGH):\(300\,\text{mg/L}\div 17.9\,(\text{mg/L\ per\ dGH})\approx \mathbf{16.8}\,
\mathbf{dGH}\)
The General Hardness (GH) of natural seawater is typically much higher than 300 ppm, generally around
6,570 ppm (parts per million). Therefore, your reading of GH 300 ppm in seawater suggests the water may be diluted or formulated incorrectly, which could be problematic for sea cucumbers.
Seawater GH and Sea Cucumbers
Natural Seawater Hardness: Seawater is inherently "very hard" due to high concentrations of dissolved minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium ions. A typical GH value is about 6,570 ppm.
300 ppm GH in Seawater: This level of GH is characteristic of hard freshwater (approximately 16.7 dGH) or brackish water, not full-strength seawater.
Sea Cucumber Tolerance: Sea cucumbers (echinoderms) have limited adaptability to significant salinity changes and require stable water parameters. Their optimal environment is full-strength seawater, typically with a salinity range of 30-34 parts per thousand (ppt), which corresponds to a much higher GH.
Potential Issues: The 300 ppm GH level indicates a low mineral concentration (and likely low salinity). This suboptimal condition can cause osmotic stress, weaken the sea cucumber's immune system, and negatively affect growth and survival.
Recommended Action
You should focus on maintaining proper salinity as the primary water parameter for sea cucumbers, as GH measurements for marine systems are not standard or practical due to the high mineral content.
Measure Salinity: Use a refractometer or hydrometer to measure the salinity (or specific gravity) of the water.
Target Range: Aim for a salinity of 30 to 34 ppt (parts per thousand) for optimal health and survival.
Adjust Water: If your salinity is low, gradually increase it using a quality marine salt mix.
Monitor other parameters: Ensure other critical water parameters like temperature, pH (7.6-8.4), and dissolved oxygen are within acceptable ranges for sea cucumbers
# Purse Saine
The conversion factor between these units is approximately:1 °dH (dGH) = 17.9 mg/L (ppm) as CaCO₃
Given a GH of 300 mg/L (which is also 300 ppm), the conversion is as follows: GH in mg/L (as CaCO₃):300 mg/L (or 300 ppm)
GH in degrees German Hardness (°dH or dGH):\(300\,\text{mg/L}\div 17.9\,(\text{mg/L\ per\ dGH})\approx \mathbf{16.8}\,
\mathbf{dGH}\)
The General Hardness (GH) of natural seawater is typically much higher than 300 ppm, generally around
6,570 ppm (parts per million). Therefore, your reading of GH 300 ppm in seawater suggests the water may be diluted or formulated incorrectly, which could be problematic for sea cucumbers.
Seawater GH and Sea Cucumbers
Natural Seawater Hardness: Seawater is inherently "very hard" due to high concentrations of dissolved minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium ions. A typical GH value is about 6,570 ppm.
300 ppm GH in Seawater: This level of GH is characteristic of hard freshwater (approximately 16.7 dGH) or brackish water, not full-strength seawater.
Sea Cucumber Tolerance: Sea cucumbers (echinoderms) have limited adaptability to significant salinity changes and require stable water parameters. Their optimal environment is full-strength seawater, typically with a salinity range of 30-34 parts per thousand (ppt), which corresponds to a much higher GH.
Potential Issues: The 300 ppm GH level indicates a low mineral concentration (and likely low salinity). This suboptimal condition can cause osmotic stress, weaken the sea cucumber's immune system, and negatively affect growth and survival.
Recommended Action
You should focus on maintaining proper salinity as the primary water parameter for sea cucumbers, as GH measurements for marine systems are not standard or practical due to the high mineral content.
Measure Salinity: Use a refractometer or hydrometer to measure the salinity (or specific gravity) of the water.
Target Range: Aim for a salinity of 30 to 34 ppt (parts per thousand) for optimal health and survival.
Adjust Water: If your salinity is low, gradually increase it using a quality marine salt mix.
Monitor other parameters: Ensure other critical water parameters like temperature, pH (7.6-8.4), and dissolved oxygen are within acceptable ranges for sea cucumbers
# Purse Saine


graph LR
%% This is a comment!!!
%% Apple Cedar Vinegar
ACV["Apple cider Vinegar"] --->UF["Unfilter vinegar"]
ACV --->F["Filter Vinegar"]
graph LR
%% This is a comment!!!
%% Coffee process
Coffee["Red Cheery ripe handpick"] ---> P1["sorted size
and sun dry"] ---> P2["storage or
need to remove the skin"] P2 ---> P3["greem bean
still have membrance coffee"] ----> R1["Light roasting
remove membrance"] R1 ---R2["Roasting for demand"]
and sun dry"] ---> P2["storage or
need to remove the skin"] P2 ---> P3["greem bean
still have membrance coffee"] ----> R1["Light roasting
remove membrance"] R1 ---R2["Roasting for demand"]
graph LR
%% This is a comment!!!
%% Pelabuhan di Batam
A[fas:fa-ship Tajuh Biru Mon & Thu
Lingga] --> B0[fas:fa-ship 🦞🐟frozen/live
Belakang Padang
Batam] -- Singapore GST 9.00%--> S0[/"Singapore GST 9.00+ import tax?
Jurong fish port(30% import)
Singapore"/] --logistic cost + 2.00SGD -->S1[/Closed March 2024
Senoko Fishery Port
Singapore/] B1[fas:fa-ship 🦞🐟 frozen/live
Sagulung daily
Batam] --freight charge 18SGD 100cm x 50cm x 50cm \( 50~90 kg\) -->S0 J1["fas:fa-ship Pelabuhan Hasim
Balerang, Batam"] <---->|Private Boat 00:45, 16.00km?| P["Ke Pulauan Petong 🥽"] J7["fas:fa-ship Pel. Pari Jembatan 6
Batam"] <---->|Private Boat 00:45, 16.00km?| PB["Pulan Benan 🥽"] J7 <-->A TPunggur["fas:fa-ship Pelabuhan Telaga Punggur
Batam"] <---->|01:45?| PB <---> |00:45 | A J6["fas:fa-ship Pel. Kepri Coral
Batam"]<-->P TP["fas:fa-ship Tanjung Pinang"] <-- Public --> A style S1 fill:red click A "https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSfVlANgYbnoqzFn5tKd4520MAiF10Sgqg343FKI2oTYmhcP8Q/viewform?usp=sharing" "budiday lobster" click P "https://batamnewsasia.com/2024/11/11/explore-pulau-petong-batams-underwater-paradise-for-tourists/" "Pulau Petong" click B1 "https://www.google.com/maps/d/edit?mid=1k7qpHqVpCqY_taRwkaVSyDc8yo8jmFo&usp=sharing" "Pel Sagulung bpk Hamzah" click TPunggur "https://www.tiketkapal.com/" "Ferry ke pulau"
Lingga] --> B0[fas:fa-ship 🦞🐟frozen/live
Belakang Padang
Batam] -- Singapore GST 9.00%--> S0[/"Singapore GST 9.00+ import tax?
Jurong fish port(30% import)
Singapore"/] --logistic cost + 2.00SGD -->S1[/Closed March 2024
Senoko Fishery Port
Singapore/] B1[fas:fa-ship 🦞🐟 frozen/live
Sagulung daily
Batam] --freight charge 18SGD 100cm x 50cm x 50cm \( 50~90 kg\) -->S0 J1["fas:fa-ship Pelabuhan Hasim
Balerang, Batam"] <---->|Private Boat 00:45, 16.00km?| P["Ke Pulauan Petong 🥽"] J7["fas:fa-ship Pel. Pari Jembatan 6
Batam"] <---->|Private Boat 00:45, 16.00km?| PB["Pulan Benan 🥽"] J7 <-->A TPunggur["fas:fa-ship Pelabuhan Telaga Punggur
Batam"] <---->|01:45?| PB <---> |00:45 | A J6["fas:fa-ship Pel. Kepri Coral
Batam"]<-->P TP["fas:fa-ship Tanjung Pinang"] <-- Public --> A style S1 fill:red click A "https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSfVlANgYbnoqzFn5tKd4520MAiF10Sgqg343FKI2oTYmhcP8Q/viewform?usp=sharing" "budiday lobster" click P "https://batamnewsasia.com/2024/11/11/explore-pulau-petong-batams-underwater-paradise-for-tourists/" "Pulau Petong" click B1 "https://www.google.com/maps/d/edit?mid=1k7qpHqVpCqY_taRwkaVSyDc8yo8jmFo&usp=sharing" "Pel Sagulung bpk Hamzah" click TPunggur "https://www.tiketkapal.com/" "Ferry ke pulau"
flowchart TB
subgraph OCEAN9 ["fas:fa-ship OCEAN 9 "]
direction LR
TP([Telaga Punggur])-->|ferry 11:00 web kapaltiket.com| A([BENAN]) --> |"00:45"| B([Tajuh Biru]) --> C(["Sei Tenam"]) --> D(["Senayang"]) <--->|"from 07:15 Pancur"| E(["Pancur"])
end
subgraph DRAGON5 ["fas:fa-ship DRAGON 5"]
direction LR
TP1(["Telaga punggur"]) --> CC(["Sei Tenam"])-->JG(["Jagoh"])
end
subgraph Anambas ["fas:fa-ship Anambas"]
direction LR
TP2(["Telaga Punggur"]) --"Rp. 494k"--> Letung --"Rp 495k"--> Terempa(["Terempa"])
end
subgraph Bintan["Pulau Bintan/Tanjung Pinang"]
direction LR
BTP(["Tanjung Pinang"])
end
TP <--.--> TP1 <--.--> TP2
style A fill: black, color: white
style B fill:grey, color:#fff
style TP fill:blue, color: whit
style TP1 fill:blue, color: white
style TP2 fill:blue, color: white
click BTP "https://www.welcometobintan.com/images/map.jpg" "Tanjung Pinang"
%%{init: {"pie": {"textPosition": 0.5}, "themeVariables": {"pieOuterStrokeWidth": "5px"}} }%%
pie title International Reserves Of Central Banks Worldwide
"US" :58.4
"Euro" : 20.50
"Chinese RMB" : 2.7
"Japanese Yen": 5.5
"Pound Sterling": 4.9
"Australian Dollars": 2.0
"Canadian Dollar": 2.4
"Other Currencies": 3.5
pie title Investment weighting factor
"Money" :60
"Labour" : 35
"Technology-Consultant" : 5
timeline
%% https://ikanbilis.com.my/
title Panen anchovies di Lingga
Jan
: Weather/wet/highwave
Feb
: Weather/wet/highwave
Mar
: Weather/wet/highwave
Apr
: Squid/Anchovies
May
: Squid/Anchovies
Jun
: Squid/Anchovies
Jul
: Squid/Anchovies
Aug
: Squid/Anchovies
Sep
: Squid/Anchovies
Oct
: Squid/Anchovies
Nov
: Squid/Anchovies
Dec
: weather/wet/highwave
: Lobster/udang kara/banana shrimp
withdraw: next years with draw get 1 dollars
up to 6 years before can get as according to percentage
profit allocate 20% profit forfuture reinvestment
money(60%) | labor (40%-->
Manager(60%) + worker(40%)| Calculation
Propotion| |-------|-------------|------|-------------| | A | 100K x 0.6 | 0 | 100K/200K*0.6=0.3 | | B | 100K x 0.6 | 0.4 x 0.6=0.24|30% +24%=54%| | C | 0 | 0.4 x 0.4=0.16 | 16% | Kerapu Cantang Hitam vs. Kerapu Cantang Kuning Kerapu Cantang adalah hasil hibridisasi (persilangan buatan) antara Kerapu Macan (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus) betina dan Kerapu Kertang (Epinephelus lanceolatus) jantan. Namun, terdapat variasi warna pada kerapu cantang, seperti hitam dan kuning, yang dipengaruhi oleh faktor genetik dan lingkungan. Perbedaan Kerapu Cantang Hitam vs. Kuning Kriteria Kerapu Cantang Hitam Kerapu Cantang Kuning Warna Tubuh Dominan hitam atau abu-abu gelap dengan bercak hitam Dominan kuning keemasan dengan bercak cokelat atau hitam Pertumbuhan Cenderung lebih cepat Sedikit lebih lambat dibanding hitam Harga Pasar Biasanya lebih tinggi karena permintaan lebih besar Sedikit lebih murah Kandungan Gizi Sama (tinggi protein, rendah lemak) Sama (tinggi protein, rendah lemak) Rasa & Tekstur Daging lebih padat, cocok untuk bakar & kukus Daging lembut, cocok untuk sup & tumis Ketahanan Penyakit Lebih tahan terhadap stres lingkungan Sedikit lebih rentan terhadap perubahan kualitas air Faktor yang Mempengaruhi Warna Genetik – Variasi gen dari indukan memengaruhi pigmentasi. Pakan – Kandungan astaxanthin (pigmen karotenoid) dalam pakan dapat memperkuat warna kuning. Lingkungan – Kualitas air, intensitas cahaya, dan substrat tambak memengaruhi warna. Kesimpulan Kerapu Cantang Hitam lebih populer di pasar karena pertumbuhannya cepat dan warna yang menarik. Kerapu Cantang Kuning memiliki keunikan warna yang cocok untuk hidangan tertentu. Keduanya sama-sama bernilai ekonomis tinggi dan banyak dibudidayakan di Indonesia. Jika Anda ingin membudidayakan atau membelinya, pilih sesuai preferensi pasar atau kebutuhan kuliner. 🐟🔥 # Endoscope 1. Diameter (8.0mm vs. 7.00mm)- one lense and 2 lenses Feature 8.0mm Endoscope 7.00mm Endoscope Size Slightly thicker More slender Flexibility Less flexible More flexible Applications Better for larger gaps (e.g., pipes, automotive) Better for tight spaces (e.g., electronics, narrow pipes) Key Takeaway: 7.00mm is better for confined spaces (e.g., engine crevices, plumbing). 8.0mm may offer better durability due to thicker construction.